Spring AI has experienced significant advancements in its recent versions, making it a powerful tool for developers and data scientists. In this blog, we aim to give a high level introduction. This will help you connect with AI offerings from two major cloud providers: Azure and AWS.
Both Azure and AWS offer a variety of artificial intelligence models that cater to different needs and applications. We will explore the features of two distinct large language models (LLMs) from these cloud platforms. We will also discuss how they can be integrated into your projects. By the end of this exploration, you will understand better how to use these powerful AI models. You can leverage them within the Spring AI framework.
Azure Integration – pom entry
Quickest integration for a chat model of integration is from Azure. For integration of Azure, these are the pom entries that will be needed
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-azure-openai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
AWS bedrock Integration – pom entry
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-bedrock-ai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
When you provision the Azure AI services. Here is a sample screen look alike for the provisioned service
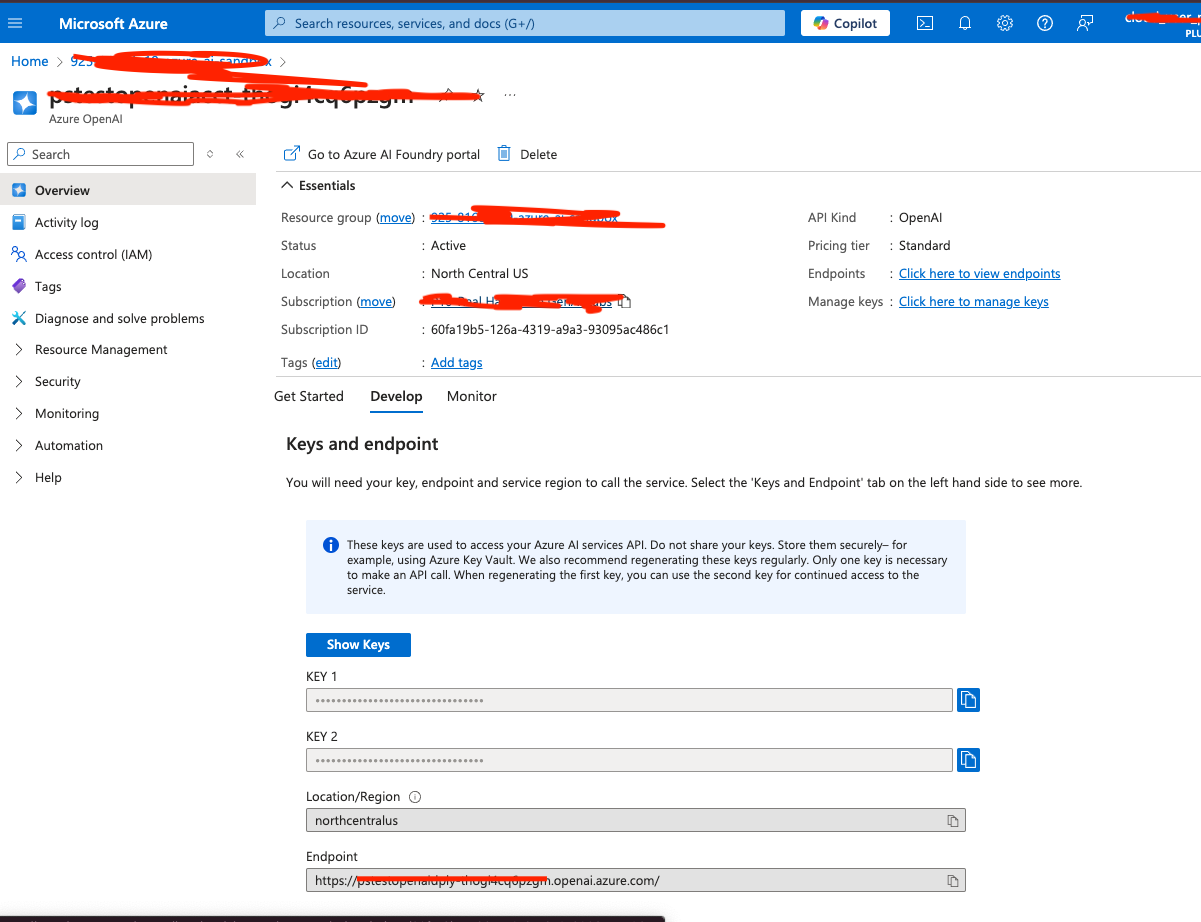
As shown keep a note of the key, URL information for the spring properties file. I’m using a restricted cloud sandbox, the only LLM model that I can use is the gpt-35-turbo model
spring.ai.azure.openai.chat.enabled=true
spring.ai.azure.openai.endpoint=${AZURE_ENDPOINT}
spring.ai.azure.openai.api-key=${AZURE_API_KEY}
spring.ai.azure.openai.chat.options.model=gpt-35-turbo
For the AWS bedrock integration, you will need the AWS secret ID and key information. Here are the entries in spring properties file

spring.ai.bedrock.aws.region=us-east-1
spring.ai.bedrock.aws.access-key=${AWS_ACCESS_KEYID}
spring.ai.bedrock.aws.secret-key=${AWS_SECRET_KEY}
spring.ai.bedrock.jurassic2.chat.enabled=true
spring.ai.bedrock.jurassic2.chat.options.temperature=0.8
spring.ai.bedrock.titan.embedding.enabled=true
spring.ai.bedrock.titan.embedding.model=amazon.titan-embed-image-v1
Autowire the templates given by spring framework in the constructor. Here is a sample service hooking up all the classes
/**
* Constructor to initialize the chat model and environment
*
* @param chatModel
* @param environment
* @param bedrockAi21Jurassic2ChatModel
*/
public SathishChatService(AzureOpenAiChatModel chatModel, Environment environment, BedrockAi21Jurassic2ChatModel bedrockAi21Jurassic2ChatModel, BedrockTitanEmbeddingModel embeddingModel) {
logger.info("Chat Service Initialized");
this.environment = environment;
this.azureOpenAiChatModel = chatModel;
this.embeddingModel = embeddingModel;
this.bedrockAi21Jurassic2ChatModel =
bedrockAi21Jurassic2ChatModel;
}
We see the AzureOpenAIChatModel in the code block. The Azure Open AI related chat model is injected into it. Code also injects the Bedrock Jurrasic 2 and Titan Model into the service.
The AzureOpenAIChatModel and the Bedrock chat offer similar functionality, and here is the integration calls for both the chat models. The Azure integration looks something like this
public RunData getAzureAIResponse(String year) {
var message = """
Please give me all the marathons for the year {year}. Also provide the location and the date of the marathon.
If you don't know the answer, just say "I don't know" {format}""";
var listOutputParser = new BeanOutputConverter<>(RunData.class);
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(message, Map.of("year", year, "format", listOutputParser.getFormat()));
Prompt prompt = promptTemplate.create(AzureOpenAiChatOptions.builder()
.withDeploymentName(environment.getProperty(AZURE_DEPLOYMENT_NAME)).build());
ChatResponse chatResponse = azureOpenAiChatModel.call(prompt);
RunData runData = listOutputParser.convert(chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getContent());
return runData;
}
This is the AWS response.
public RunData getAWSAIResponse(String year) {
var message = """
Please give me all the marathons for the year {year}. Also provide the location and the date of the marathon.
If you don't know the answer, just say "I don't know" {format}""";
var listOutputParser = new BeanOutputConverter<>(RunData.class);
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(message, Map.of("year", year, "format", listOutputParser.getFormat()));
Prompt prompt = promptTemplate.create(BedrockTitanChatOptions.builder().build());
ChatResponse chatResponse = bedrockAi21Jurassic2ChatModel.call(prompt);
RunData runData = listOutputParser.convert(chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getContent());
return runData;
}
Both techniques return a record called RunData. Here is the snippet for the RunData record class. The new Spring AI version has made the output information to be converted to a Bean using the BeanOutputConverter.
record RunData(String name, List<CityDate> cityAndDate) {
}
record CityDate(String location, String date) {
}
The Azure Controller class looks something like this
@RestController
class RunsAzureController {
final SathishChatService chatService;
public RunsAzureController(SathishChatService chatService) {
this.chatService = chatService;
}
@GetMapping("/topAzureMarathons")
public RunData getChatResponseForTopMarathons(@RequestParam(value = "year", defaultValue = "2023") String year) {
return chatService.getAzureAIResponse(year);
}
}
The AWS Bedrock controller looks something like this
@RestController
class RunAWSController {
final SathishChatService chatService;
public RunAWSController(SathishChatService chatService) {
this.chatService = chatService;
}
@GetMapping("/topAWSMarathons")
public RunData getChatResponseForTopMarathons(@RequestParam(value = "year", defaultValue = "2023") String year) {
return chatService.getAWSAIResponse(year);
}
}
The amount of boilerplate code Spring AI can abstract from development is significant. This is the important information to note. Both the controllers reuse the same service class and the boilerplate to get injected for the individual classes. The prompts’ reuse is the best way to reduce code variability. It offers an advantage when using different LLMs. This is the advantage Spring AI provides. The framework injects the required inputs and data that is needed to the service class. If there are any exceptions connecting to the services, the framework shuts down instantly. It uses the details it needs for a successful start.
To conclude, the discussion is focused on using Spring AI and how to integrate with two cloud providers LLMs. Reuse the code that both the cloud provider LLMs understood. It provided the desired output from their respective language models.

You must be logged in to post a comment.